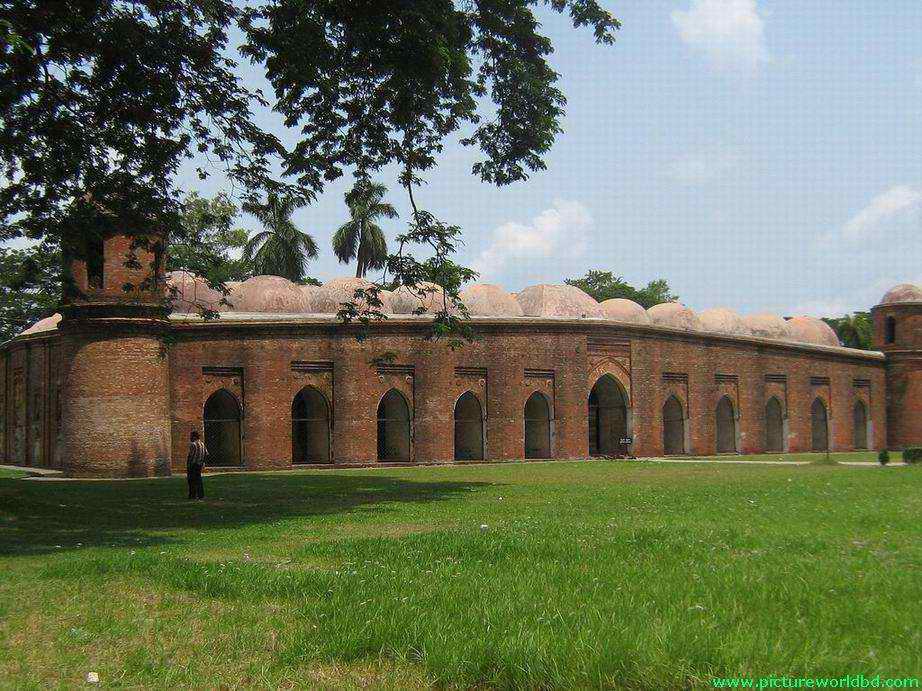
sixty dome mosque in bagerhat
n mid-15th century, a Muslim colony was founded in the unfriendly mangrove forest of the Sundarbans near the coastline in the Bagerhat district by an obscure saint-General, named Ulugh Khan Jahan. He was the earliest torch bearer of Islam in the South who laid the center of an affluent city during the reign of Sultan Nasiruddin Mahmud Shah (1442-59), then known as ‘Khalifalabad’ (present Bagerhat). Khan Jahan aborned his city with numerous mosques, tanks, roads and other public buildings, the spectacular ruins of which are focused around the most imposing and largest multidomed mosques in Bangladesh, known as the Shait-Gumbad Masjid (160’X108′). The stately fabric of the monument, serene and impressive, stands on the eastern bank of an unusually vast sweet-water tank, clustered around by the heavy foliage of a low-laying countryside, characteristic of a sea-coast landscape. So in the year 1459 the great Azam Ulugh Khan Jahan established this mosque, which called Shat Gambuj Mosjid. In Bengali Shat means the number 60. Though it is called Shat Gambuj Mosjid, actually the numbers of Gamboj in the mosque are 81. The mosque roofed over with 77 squat domes, including 7 chauchala or four-sided pitched Bengali domes in the middle row. The vast prayer hall, although provided with 11 arched doorways on east and 7 each on north and south for ventilation and light, presents a dark and somber appearance inside. It is divided into 7 longitudinal aisles and 11 deep bays by a forest of slender stone columns, from which springs rows of endless arches, supporting the domes. Six feet thick, slightly tapering walls and hollow and round, almost detached corner towers, resembling the bastions of fortress, each capped by small rounded cupolas, recall the Tughlaq architecture of Delhi.
Related Portfolio
Service Offered
Monthly Calendar
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| « Jan | ||||||
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 |
| 30 | ||||||
Image Gallery